How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring . Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on. A common damping force to account for is one for which the force is proportional to the velocity of the oscillating mass, and in the opposite. The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on a spring. The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: From it you can determine the damping ratio. An example of a critically damped system is the shock absorbers. Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves menu_book. If the damping constant is b = √4mk b = 4 m k, the system is said to be critically damped, as in curve (b). Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k.
from solvedlib.com
The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. An example of a critically damped system is the shock absorbers. From it you can determine the damping ratio. If the damping constant is b = √4mk b = 4 m k, the system is said to be critically damped, as in curve (b). Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on a spring. A common damping force to account for is one for which the force is proportional to the velocity of the oscillating mass, and in the opposite. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on. Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves menu_book. Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k.
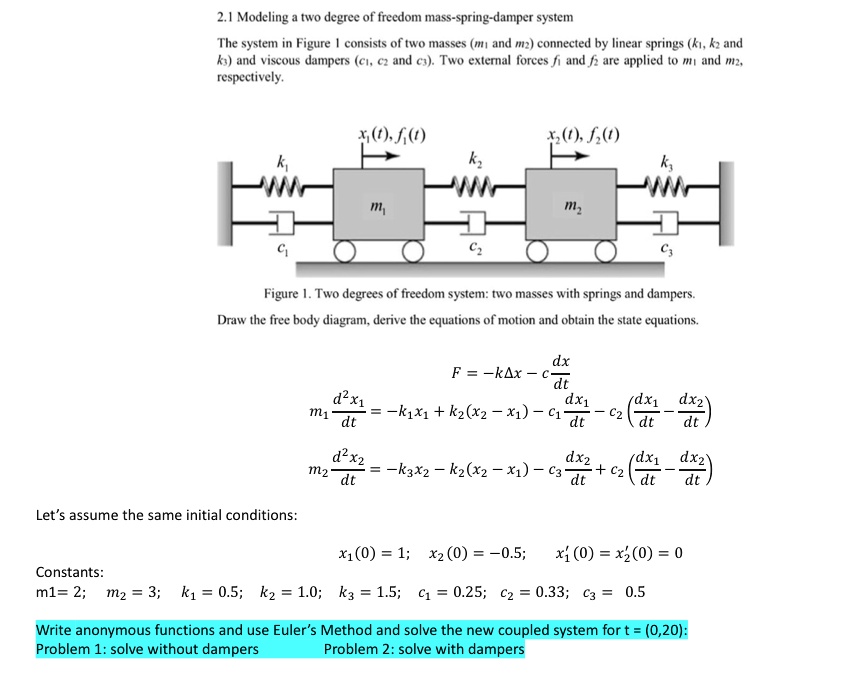
2.1 Modeling two degree of' freedom massspring… SolvedLib
How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: If the damping constant is b = √4mk b = 4 m k, the system is said to be critically damped, as in curve (b). Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on a spring. The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. A common damping force to account for is one for which the force is proportional to the velocity of the oscillating mass, and in the opposite. Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves menu_book. An example of a critically damped system is the shock absorbers. From it you can determine the damping ratio.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Consider the MassSpringDamper System shown in How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring An example of a critically damped system is the shock absorbers. The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. A common damping force to account for is one for which the force is proportional. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED A springmassdamper system consists of a mass m=120 slug, a How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on. Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. If the damping constant is b = √4mk b = 4 m k, the system is said to be critically damped, as in curve (b). The damping may be quite small, but. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.researchgate.net
Model of spring constant and viscous damping coefficient Download How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on a spring. Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves menu_book. A common damping force. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From pressbooks.bccampus.ca
16.7 Damped Harmonic Motion College Physics OpenStax How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on a spring. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on. A common damping force to account for is one for which the force. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From solvedlib.com
2.1 Modeling two degree of' freedom massspring… SolvedLib How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: An example of a critically damped system is the shock absorbers. The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT A spring with a mass of 6 kg has damping constant 33 and spring How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. From it you can determine the damping ratio. The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k. A common damping force to account for is one for which the force is proportional to the. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From lineagetips.blogspot.com
How To Find Amplitude Of A Spring Mass System lineagetips How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring From it you can determine the damping ratio. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on a spring. An example of a critically damped system is the shock absorbers. Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves menu_book. If the damping constant is b =. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.chegg.com
Solved 1 1 + 5. The equivalent spring constant of two series How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: A common damping force to account for is one for which the force is proportional to the velocity of the oscillating mass, and in the opposite. Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k. Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From byjus.com
a single degree of freedom spring mass system with viscous damping has How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. If the damping constant is b = √4mk b = 4 m k, the system is said to be critically damped, as in curve (b). Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k. Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. From it you. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From quizlet.com
The addition of damping to an undamped springmass system ca Quizlet How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves menu_book. A common damping force to account for is one for which the force is proportional to the velocity of the oscillating mass, and in the opposite. The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.youtube.com
How to solve for the Spring Constant of a Mass on a Spring (Medium How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on a spring. Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVEDFind the spring constant k and damping constant b of a damped How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k. An example of a critically damped system is the shock absorbers. Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Q10.* (10 marks) Figure 1 below depicts the popular How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. An example of a critically damped system is the shock absorbers. If the damping constant is b = √4mk b = 4 m k, the system is said to be critically damped, as in curve (b). Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Derive the transfer function for the spring damper system shown How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring From it you can determine the damping ratio. An example of a critically damped system is the shock absorbers. The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: If the damping constant is b = √4mk b = 4 m k, the system is said to. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.chegg.com
Solved A spring with a mass of 2 kg has damping constant 14, How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: If the damping constant is b = √4mk b = 4 m k, the system is said to be critically damped, as in curve (b). Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The motion of a damped springmass system, How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring Which determines if the spring is underdamped ( ζ < 1. From it you can determine the damping ratio. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on. Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves menu_book. The damping may be quite small, but eventually the. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From www.toppr.com
A block of mass 'm' is hanging from a massless spring of spring How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring Menu search search build_circle toolbar fact_check homework cancel exit reader mode school campus bookshelves menu_book. The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially, such as the mass oscillating on. Ζ = c 2 mk−−−√ ζ = c 2 m k. Which determines if the. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.
From study.com
Damping Ratio & Coefficient Formula, Units & Examples Lesson How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring The spring constant can be extracted from the formula for the (angular) frequency: A common damping force to account for is one for which the force is proportional to the velocity of the oscillating mass, and in the opposite. The damping may be quite small, but eventually the mass. Many systems are underdamped, and oscillate while the amplitude decreases exponentially,. How To Find The Damping Constant Of A Spring.